What is a Hard Acid?
Hard acids are Lewis acids that are only weakly polarizable.
Other things being approximately equal:
- hard acids react faster with hard bases and form stronger bonds with them
- soft acids react faster with soft bases and form stronger bonds with them
These observations are sometimes called the "HSAB" rule: the hard-soft acid-base rule. The 'rule' is a qualitative guide to reactions; it is not a quantitative, numerical method.
An example of HSAB is that hard acids, such as alkali metal ions, prefer to bond to hard bases, such as O- or N-, rather than their softer S- or P- analogues.
Hard - Soft Acid Ions

Image by Tem5psu
Hard - Soft Base Ions
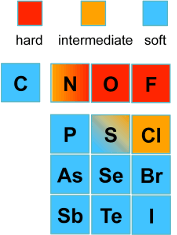
Image by Tem5psu
Further Examples of Hard Acids: BF3, BCl3, CO2, RCO+, SO3, RMgX, VO2+, AlCl3
Further Examples of Soft Acids: BH3, Br2, I2, RO+
Further Examples of Hard Bases: NH3, ROH, H2O, OH-, SO42-
Further Examples of Soft Bases: H-, R-, CO, PR3, C6H6, SCN-

